Manual Transmission Clutch⁚ An Overview
A manual transmission clutch is a vital component‚ connecting and disconnecting engine power to the gearbox. This allows gear changes and precise vehicle speed and power control. The clutch system typically includes a flywheel‚ pressure plate‚ clutch disc‚ and release bearing. Its operation is crucial for smooth driving.
The Role of the Clutch in Manual Transmissions
In a manual transmission vehicle‚ the clutch acts as the crucial intermediary between the engine’s rotating power and the transmission’s gears. Its primary function is to seamlessly engage and disengage this power transfer. When the clutch pedal is depressed‚ it disconnects the engine from the transmission‚ allowing for smooth gear changes without stalling. This controlled disengagement is essential for shifting smoothly between gears‚ preventing damage to the transmission components. Releasing the clutch pedal re-establishes the connection‚ smoothly transferring engine power to the selected gear. The clutch’s design incorporates a friction mechanism‚ which gradually transfers power to prevent sudden jolts during engagement and disengagement. The precise control the clutch offers is what distinguishes a manual transmission driving experience.
Clutch Engagement and Disengagement
Clutch engagement and disengagement are fundamental actions in operating a manual transmission vehicle. Engagement involves connecting the engine’s power to the transmission‚ allowing the car to move. This is achieved by slowly releasing the clutch pedal‚ gradually transferring power from the engine to the transmission’s gears. The driver must coordinate this release with the throttle to avoid stalling or jerking. Disengagement‚ on the other hand‚ is the process of disconnecting the engine’s power from the transmission. This is done by depressing the clutch pedal‚ separating the engine’s flywheel from the transmission’s input shaft. This allows the driver to shift gears without any power transmission‚ preventing gear damage. Smooth engagement and disengagement require practice and coordination. Improper technique can lead to premature clutch wear or damage to the transmission. The process is a key aspect of driving a manual transmission car.
Types of Clutches in Manual Transmissions
While most manual transmissions utilize a single-disc dry clutch‚ variations exist. The single-disc dry clutch is the most common type‚ employing a single friction disc that engages with the flywheel and transmission input shaft. This design is relatively simple‚ durable‚ and cost-effective. However‚ other types‚ although less prevalent‚ include dual-mass flywheels (DMFs) which reduce vibrations and improve drivability. These often incorporate a second‚ smaller flywheel connected to the main flywheel by springs. Another variation involves the use of dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs)‚ which are technically automatic transmissions with two clutches but function similarly. They provide rapid gear changes‚ but are far more complex than a standard single-disc dry clutch. The choice of clutch type depends on factors such as vehicle application‚ performance requirements‚ cost‚ and desired levels of driver control and comfort.
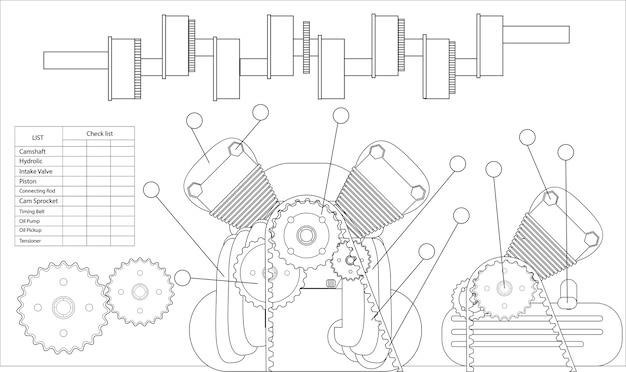
Manual Transmission Diagram⁚ Key Components
A manual transmission clutch system diagram typically shows the flywheel‚ pressure plate‚ clutch disc (friction plate)‚ release bearing (throwout bearing)‚ and the linkage connecting to the clutch pedal. Understanding these components is key to comprehending clutch operation.
Flywheel and Pressure Plate
The flywheel‚ a heavy disc attached to the engine’s crankshaft‚ stores rotational energy‚ smoothing out engine operation and providing momentum during gear changes. Its smooth surface is critical for the clutch’s function. The pressure plate is a spring-loaded component that clamps the clutch disc against the flywheel. This pressure is essential for transmitting engine torque. The pressure plate’s springs provide the clamping force‚ while its design ensures even pressure distribution across the clutch disc’s surface; Variations in pressure plate design affect clutch engagement characteristics‚ influencing smoothness and wear. A properly functioning pressure plate is crucial for consistent clutch engagement and prevents slippage. Failure of the pressure plate can result in clutch slippage‚ making gear changes difficult or impossible. Regular inspection and maintenance of the pressure plate are recommended to prevent premature wear and ensure optimal performance of the entire clutch assembly. The interaction between flywheel and pressure plate forms the foundation of power transmission in a manual transmission system.
Clutch Disc (Friction Plate)
The clutch disc‚ or friction plate‚ is positioned between the flywheel and the pressure plate‚ acting as the intermediary in power transmission. It’s a critical component with a layered structure⁚ a friction material bonded to both sides of a steel hub. This design allows the disc to rotate freely when the clutch is disengaged and to firmly grip the flywheel when engaged‚ transferring engine power to the transmission. The friction material‚ typically organic‚ ceramic‚ or metallic‚ is carefully selected for its ability to withstand high temperatures and friction while providing consistent engagement. The wear characteristics of the friction material affect clutch lifespan and performance. A worn clutch disc will exhibit slippage‚ making smooth gear changes impossible and potentially damaging other transmission components. Regular inspections are crucial to identify wear patterns and prevent failure‚ helping maintain smooth operation and prolonging the life of the entire clutch system. The clutch disc’s condition directly impacts driving experience and vehicle performance.
Release Bearing and Throwout Bearing
The release bearing‚ also known as the throwout bearing‚ is a crucial component facilitating clutch disengagement. Located within the clutch housing‚ it’s a small‚ self-lubricated bearing that presses against the pressure plate’s fingers when the clutch pedal is depressed. This action disengages the pressure plate from the clutch disc‚ allowing the engine and transmission to rotate independently. The release bearing’s design ensures smooth‚ consistent operation‚ preventing harsh engagement or disengagement. The bearing’s movement is controlled by the clutch fork‚ which directly receives force from the clutch pedal. Wear or failure of the release bearing can manifest as noisy operation‚ difficulty shifting gears‚ or complete clutch failure. Regular inspection‚ along with replacement as part of clutch maintenance‚ is crucial for sustained smooth operation and optimal performance. A failing release bearing can impact driveability and potentially damage other components‚ highlighting its importance in the overall clutch system.
Understanding the Clutch Pedal Mechanism
The clutch pedal’s function is to control clutch engagement and disengagement. This involves a linkage system or a hydraulic system connecting the pedal to the release bearing. Proper pedal operation is essential for smooth gear changes.
Clutch Pedal Linkage
In vehicles employing a mechanical clutch linkage‚ the driver’s input on the clutch pedal initiates a chain reaction. This starts with the pedal itself‚ which is connected to a linkage system‚ often consisting of rods‚ levers‚ and pivoting joints. This physical connection transmits the force from the pedal to the clutch release mechanism; The linkage’s design may vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model‚ but the basic principle remains the same⁚ translating the driver’s foot pressure into mechanical movement at the clutch. Wear and tear on the linkage components‚ such as worn bushings or bent rods‚ can lead to imprecise clutch engagement or a spongy pedal feel‚ requiring adjustments or replacements. Regular inspection and lubrication of these components are key to maintaining smooth and effective clutch operation. A malfunctioning clutch linkage can manifest as difficulty engaging or disengaging the clutch‚ making gear shifting difficult or impossible. Therefore‚ maintaining the linkage in good condition is vital for safe and efficient driving.
Hydraulic Clutch System
Many modern vehicles utilize a hydraulic clutch system for smoother‚ more consistent operation. This system replaces the mechanical linkage with a hydraulic mechanism‚ transmitting force from the clutch pedal to the release bearing via hydraulic pressure. The system typically consists of a master cylinder‚ connected to the clutch pedal‚ and a slave cylinder‚ located near the transmission. When the driver depresses the clutch pedal‚ the master cylinder piston moves‚ creating hydraulic pressure in the system. This pressure is transmitted through hydraulic lines to the slave cylinder. The slave cylinder’s piston then pushes against the release bearing‚ disengaging the clutch. This system offers advantages such as reduced pedal effort and improved feel. However‚ it’s crucial to maintain proper fluid levels and inspect for leaks. A leak in the hydraulic lines can significantly impact clutch performance‚ leading to incomplete disengagement or a very hard pedal. Regular servicing‚ including fluid changes and inspections‚ is vital for the longevity and reliability of a hydraulic clutch system.
Clutch Master and Slave Cylinders
In a hydraulic clutch system‚ the master and slave cylinders are crucial components. The master cylinder is connected to the clutch pedal; when the pedal is depressed‚ the master cylinder piston moves‚ creating hydraulic pressure. This pressure is transferred through the hydraulic lines to the slave cylinder located near the transmission. The slave cylinder‚ in turn‚ uses this pressure to actuate the release bearing‚ separating the clutch disc from the flywheel. Both cylinders are essential for smooth clutch engagement and disengagement. The master cylinder’s role is to convert the driver’s pedal force into hydraulic pressure‚ while the slave cylinder converts that pressure into mechanical force to operate the release bearing. Failure of either cylinder can lead to clutch problems‚ such as difficulty shifting gears or a complete inability to disengage the clutch. Regular inspection and maintenance of these cylinders are necessary to ensure the reliable operation of the hydraulic clutch system. Symptoms of a failing master or slave cylinder can include a spongy or hard clutch pedal‚ difficulty shifting‚ or even complete clutch failure.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular clutch maintenance is vital for optimal performance and longevity. Addressing common issues promptly prevents costly repairs. This includes inspecting the clutch system for wear and tear and replacing worn components as needed.
Common Clutch Problems and Their Causes
Several common clutch problems can significantly impact a manual transmission’s performance. One frequent issue is clutch slippage‚ where the clutch disc fails to fully engage‚ leading to a loss of power and difficulty accelerating. This often stems from worn clutch friction material or a malfunctioning pressure plate‚ failing to apply sufficient force. Another problem is a noisy clutch‚ characterized by squeaking‚ grinding‚ or chattering sounds during engagement or disengagement. These noises can indicate wear in the release bearing‚ a damaged clutch disc‚ or issues within the pressure plate. Difficulty shifting gears‚ requiring excessive force or resulting in grinding‚ often points towards a worn or damaged clutch disc‚ a misaligned clutch‚ or problems with the transmission itself. Additionally‚ a clutch that engages too high or too low in the pedal travel suggests issues with the clutch cable or hydraulic system‚ requiring adjustment or repair. Finally‚ a complete clutch failure‚ resulting in the inability to engage the clutch‚ is a serious issue that demands immediate attention‚ often necessitating a complete clutch replacement. Regular inspection and maintenance are key to preventing many of these problems.
Clutch Replacement and Repair
Clutch replacement and repair are complex procedures best left to experienced mechanics. A failing clutch‚ exhibiting slippage‚ noisy operation‚ or difficulty shifting‚ necessitates professional intervention. Repair often involves replacing worn components such as the clutch disc‚ pressure plate‚ release bearing‚ or throw-out bearing. The process necessitates specialized tools and a thorough understanding of the transmission system. Improper installation can lead to further damage‚ emphasizing the importance of professional expertise. During a clutch replacement‚ the transmission may need to be removed to access the clutch assembly. This involves disconnecting various components and carefully removing the transmission to gain access to the clutch. After replacing the worn components‚ the transmission is reinstalled‚ ensuring proper alignment and functionality. Finally‚ a thorough post-repair inspection is crucial to ensure smooth operation and prevent future issues. Ignoring clutch problems can lead to more extensive and costly repairs.
Regular Clutch Maintenance
While a manual transmission clutch is a robust component‚ regular maintenance significantly extends its lifespan and prevents premature failure. Avoid harsh starts and sudden stops‚ which put excessive stress on the clutch system. Smooth gear changes are key; avoid riding the clutch pedal (partially depressing it while driving). This practice causes unnecessary wear and tear on the clutch components. Regularly inspect the clutch fluid level (if a hydraulic system is used) and condition. Low fluid levels or contaminated fluid indicate potential problems requiring professional attention. Periodically inspect the clutch cable (if a cable-operated system) for wear‚ fraying‚ or proper adjustment. A loose or damaged cable can affect clutch engagement and disengagement. Professional inspection during routine vehicle servicing can detect subtle issues before they escalate into major problems. Early detection allows for timely intervention‚ preventing costly repairs. Proper driving habits are the most effective form of clutch maintenance‚ alongside routine inspections and professional servicing.
